11. Treatment of Psychological Disorders (Ch 16)
11.1 Insight Therapies: Psychodynamic and Humanistic Approaches
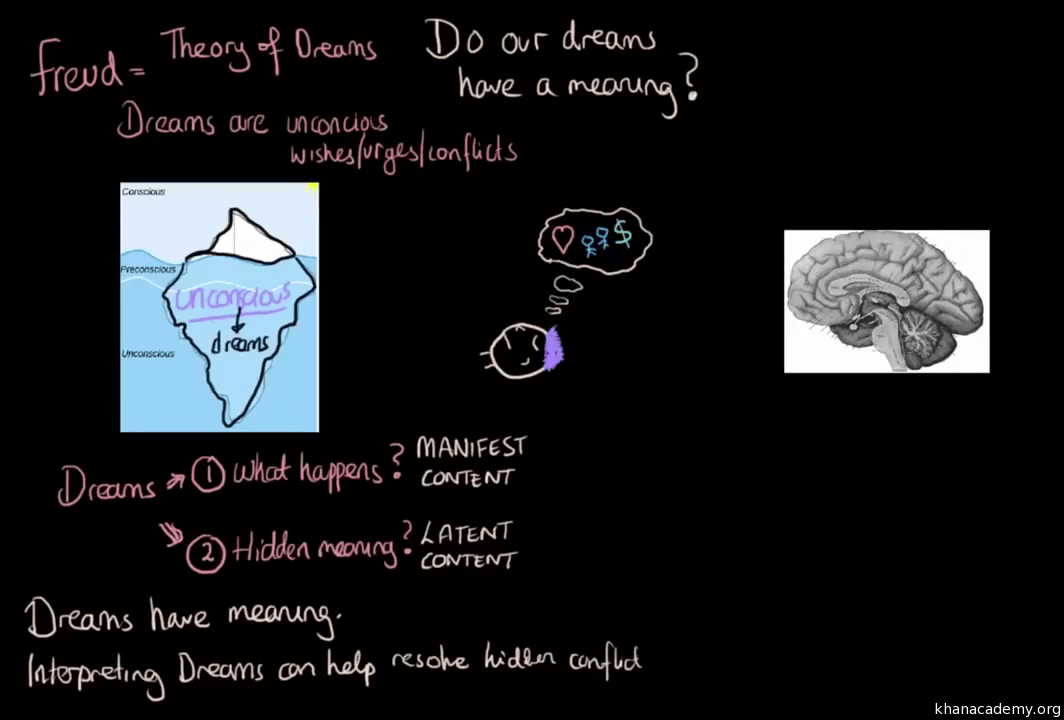
Psychodynamic
- First practiced by Freud
- Free-association
- exploring the unconscious
- says whatever comes to mind, no matter how trivial or embarrassing
- reveal repressed and unconscious thoughts
- insight and awareness
- Resolution of past conflicts
Dream analysis
- Manifest content: actual dream content
- Latent content: meaning of dream
Insight and Catharsis
- Insights: the congnitive shifts in awareness that are produced by the catharsis
- Catharsis: release of emotions during psychodrama
- Resistance
- "I have nothing to talk about today."
- coming late to a session
- not showing up to a session,
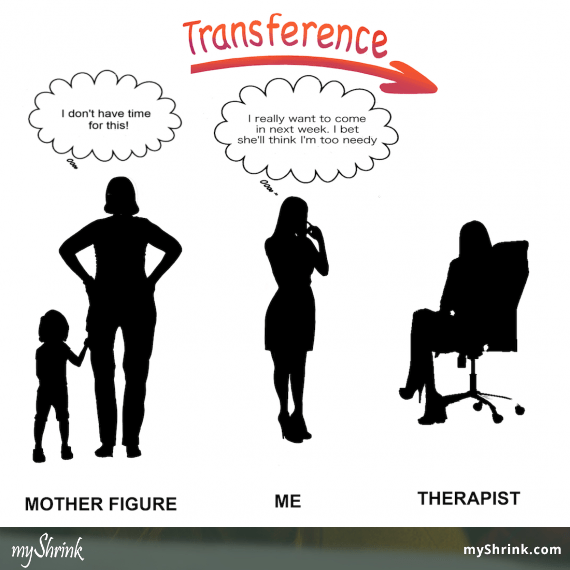
Transference
- the patient transfers all the positive or negative emotions associated with the patient’s other relationships to the psychoanalyst
Defense Mechanisms
- Repression & Denail
Humanistic
Client-centered therapy
- Carl Rogers
- active listening
- non-directive
- client makes interpretations, not therapist

Self-awareness and self acceptance
- results in personal growth
- Unconditional positive regard
- Nonjudgmental

11.2 Biological and Drug Therapies
Drugs or surgery to alter brain functioning
Psychotropic medications
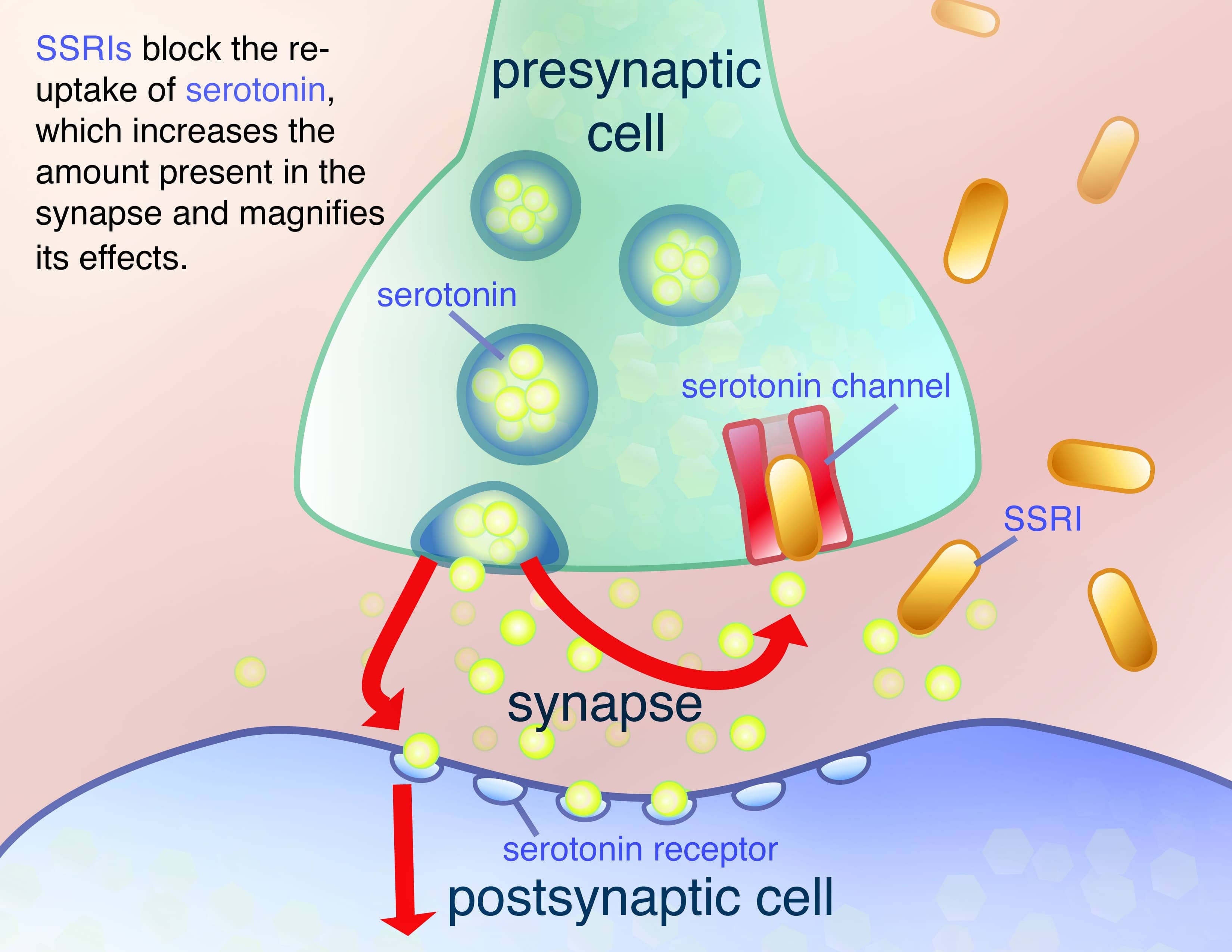
antidepressants
- SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor)
- prevent reuptake of serotonin
anti-anxiety
- reduce arousal of central nervous system
antipsychotics
- block dopamine
ECT - Electroconvulsive Therapy
Very severe
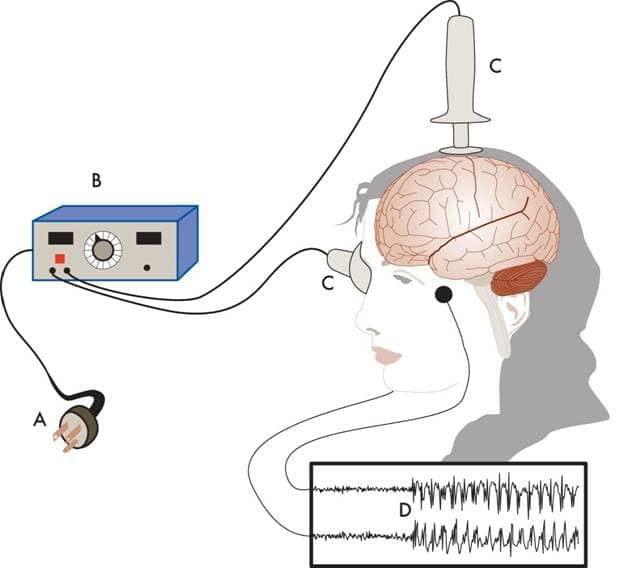
Deep Brain Stimulation
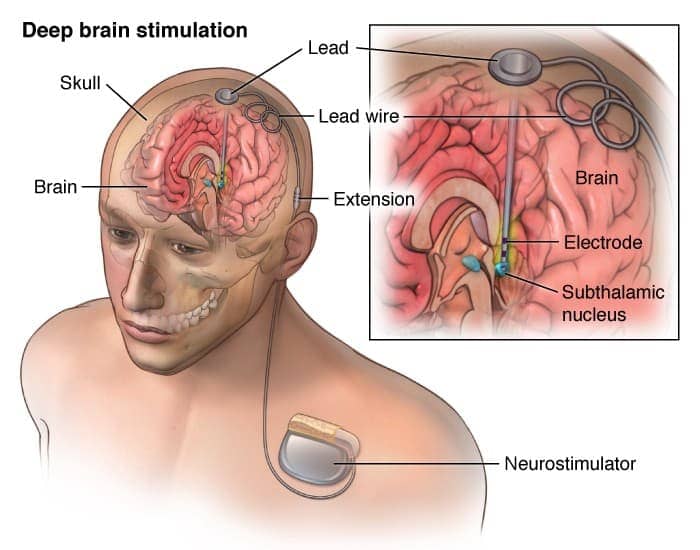
Psychosurgery
- prefrontal lobotomy (no longer used)
11.3 Behavioral Therapies
Behavior modification
- a therapist employs principles of learning to help clients change undesirable behaviors
Counterconditioning
- a client learns a new response to a stimulus that has previously elicited an undesirable behavior
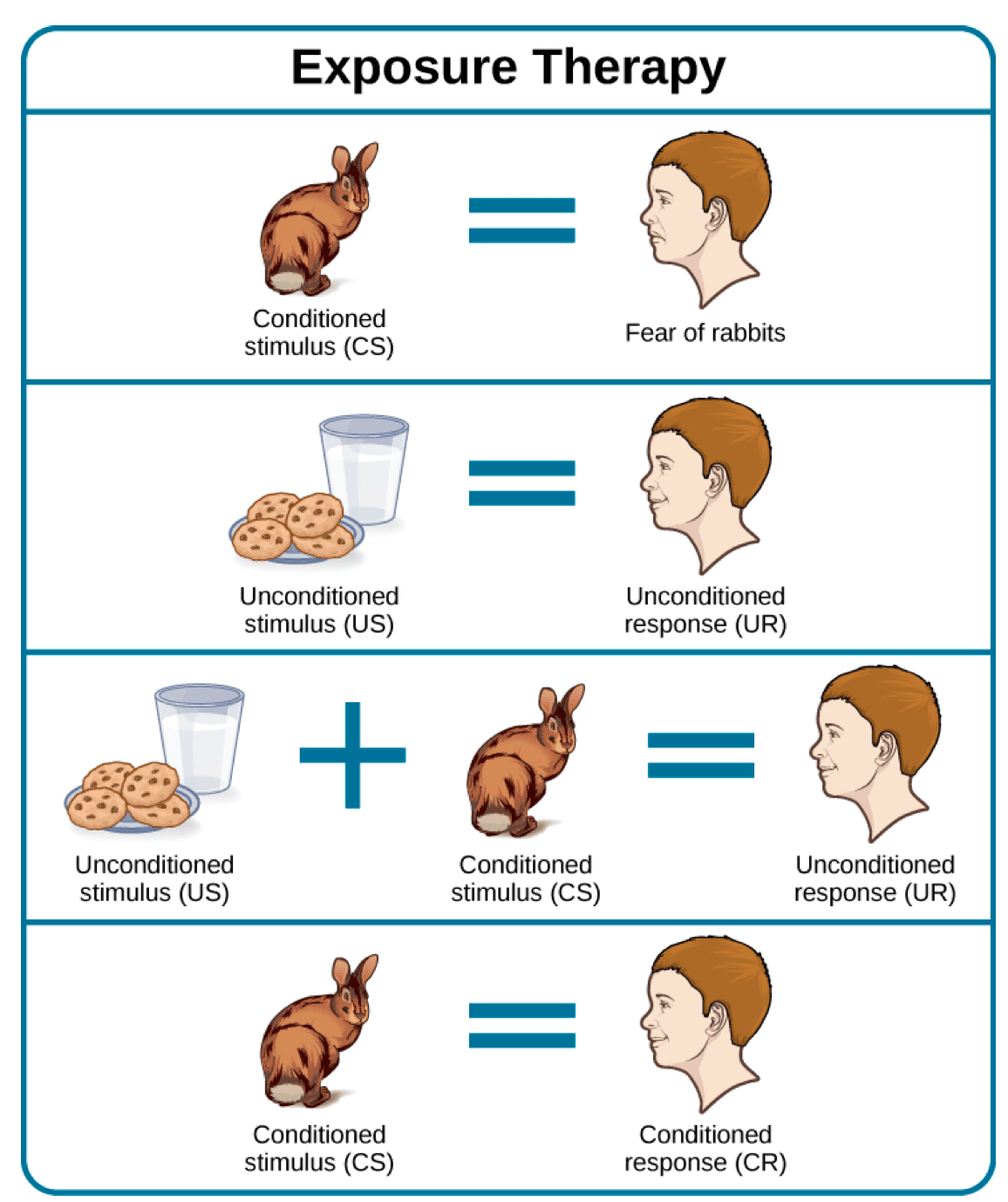
exposure therapy
- systematic desensitization
- flooding

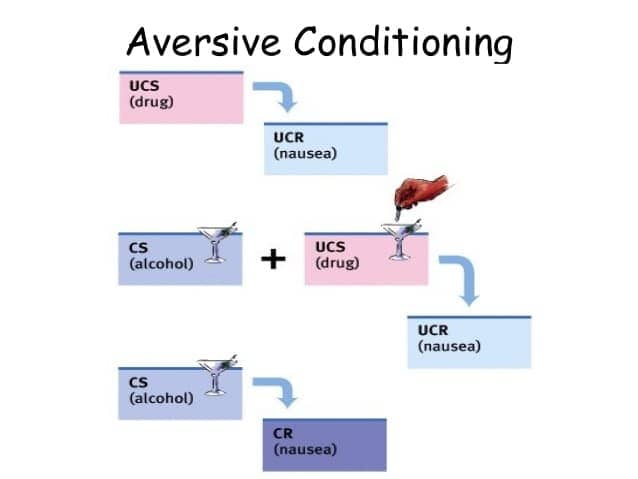
aversive conditioning
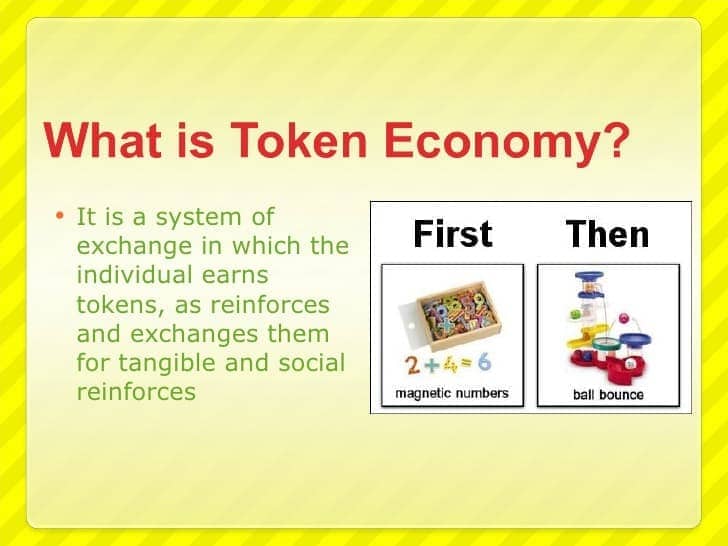
Token economy
- individuals are reinforced for desirable behaviors with tokens, such as a poker chip, that can be exchanged for items or privileges
reward based
11.4 Cognitive Therapies
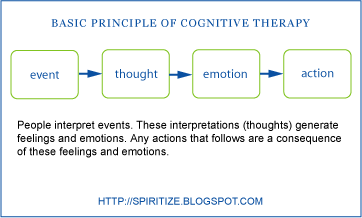
How you think determines how you feel and act
Change dysfunctional thoughts to relieve distress
Cognitive distortion
misinterpretation of a situation
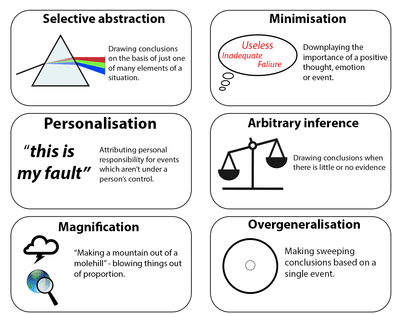
Find a more positive, realistic outlook
11.5 Community and Preventative Approaches
utilizing the resources of a community can be quite impactful to help alleviate or at least support those symptoms and those people suffering from psychological symptoms.
Behavior as an adaptation of resources and circumstances
- Individuals context in community and larger society
- Person-environment fit
- political, cultural and environmental influences-cultural diversity
- Emphasis on strengths and competencies

Quiz
- A treatment technique, often used to treat phobias, that builds upon the principles of classical conditioning is
- (A) token economy
- (B) rational-emotive behavior therapy
- (C) systematic desensitization
- (D) the placebo effect
- (E) dream analysis
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are used primarily in the treatment of which of the following?
- (A) Antisocial personality disorder
- (B) Schizophrenia
- (C) Depression
- (D) Mania
- (E) Sleep disorders
- Which of the following kinds of therapy attempts to correct irrational beliefs that lead to psychological distress?
- (A) Behavioral
- (B) Cognitive
- (C) Existential
- (D) Gestalt
- (E) Psychoanalytic
- A psychologist using Carl Rogers’ person-centered therapy strives to ensure that clients
- (A) understand unconscious influences affecting their behavior
- (B) develop positive thought patterns
- (C) develop and use effective behavioral techniques
- (D) receive unconditional positive regard
- (E) understand their irrational beliefs